Buffered Bike Lanes
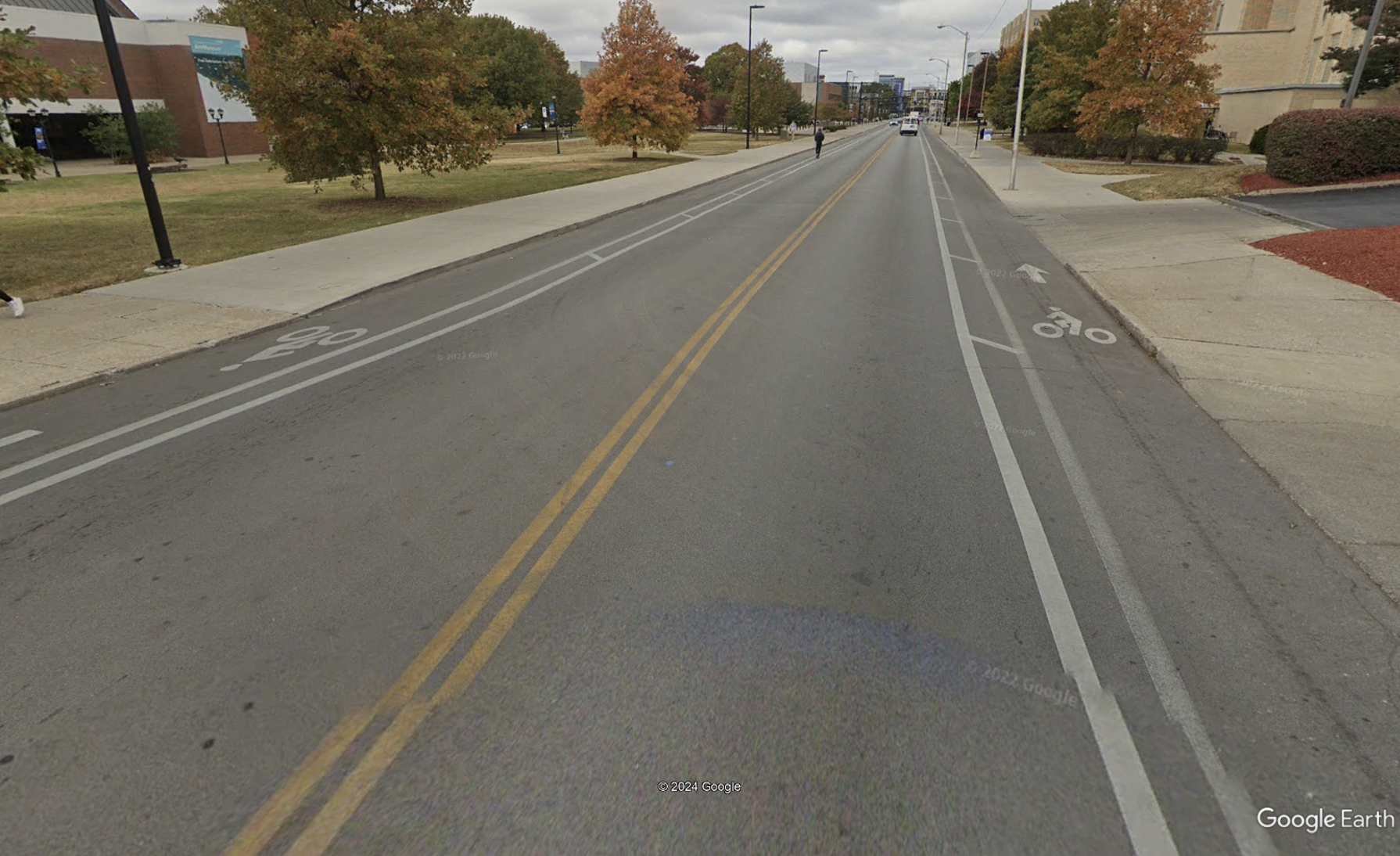

Image Source: Google Earth
DEFINITION AND DESCRIPTION
Buffered bike lanes establish a marked buffer between cyclists and vehicle traffic, which can mitigate or prevent interactions, conflicts, and crashes between bicyclists and vehicles while creating a network of safer roadways for bicycling. Consistent with the Safe System Approach principle of recognizing human vulnerability, buffered bicycle lanes separate users in space and can enhance safety for all road users.
Implementation Categories
| Area(s) | Planning, Design & Geometrics, Operations & Maintenance |
| Safety Category | 1, 2 |

CONSIDERATIONS
- Reference national guidance from the MUTCD, AASHTO’s Guide for the Development of Bicycle Facilities, and NACTO’s Urban Bikeway Design Guide when designing bicycle facilities.
- Buffers can be flush with the pavement (i.e., pavement markings) or include vertical elements (e.g., bollards, raised median). Separated bicycle lanes are buffered bicycle lanes with a vertical element of separation.
- Separated bicycle lanes are recommended on roadways with higher vehicle volumes and speeds (e.g., arterials).
- Converting traditional or flush buffered bicycle lanes to a separated bicycle lane with flexible delineator posts can reduce bicycle/vehicle crashes up to 53% (FHWA 2023).
- If raised medians are used to separate facilities, consider roadway drainage and maintenance needs.
- Memorandums of Agreement (MOA) with local governments can be used to assign maintenance responsibility for bicycle facilities.
- Buffered/Protected bike lanes is an engineering strategy in KYTC’s SHSP.
APPLICATION
- KYTC’s Complete Streets, Roads, and Highways Manual requires that bicycle lanes have a buffer on facilities with speed limits > 45 mph.
- Bicycle lanes 6 feet or wider are candidates for buffered bicycle lanes. A 2-foot buffer is preferred, and the bike lane must be at least 4 feet.
- For a buffer space greater than 3 ft wide, chevron or diagonal markings shall be applied. In buffer spaces from 2 ft to 3 ft, chevron or diagonal markings should be applied. For buffer spaces less than 2ft wide, no chevron or diagonal markings may be applied within the buffer. See MUTCD Figure 9E-6.
- Pavement markings should be thermoplastic.
example
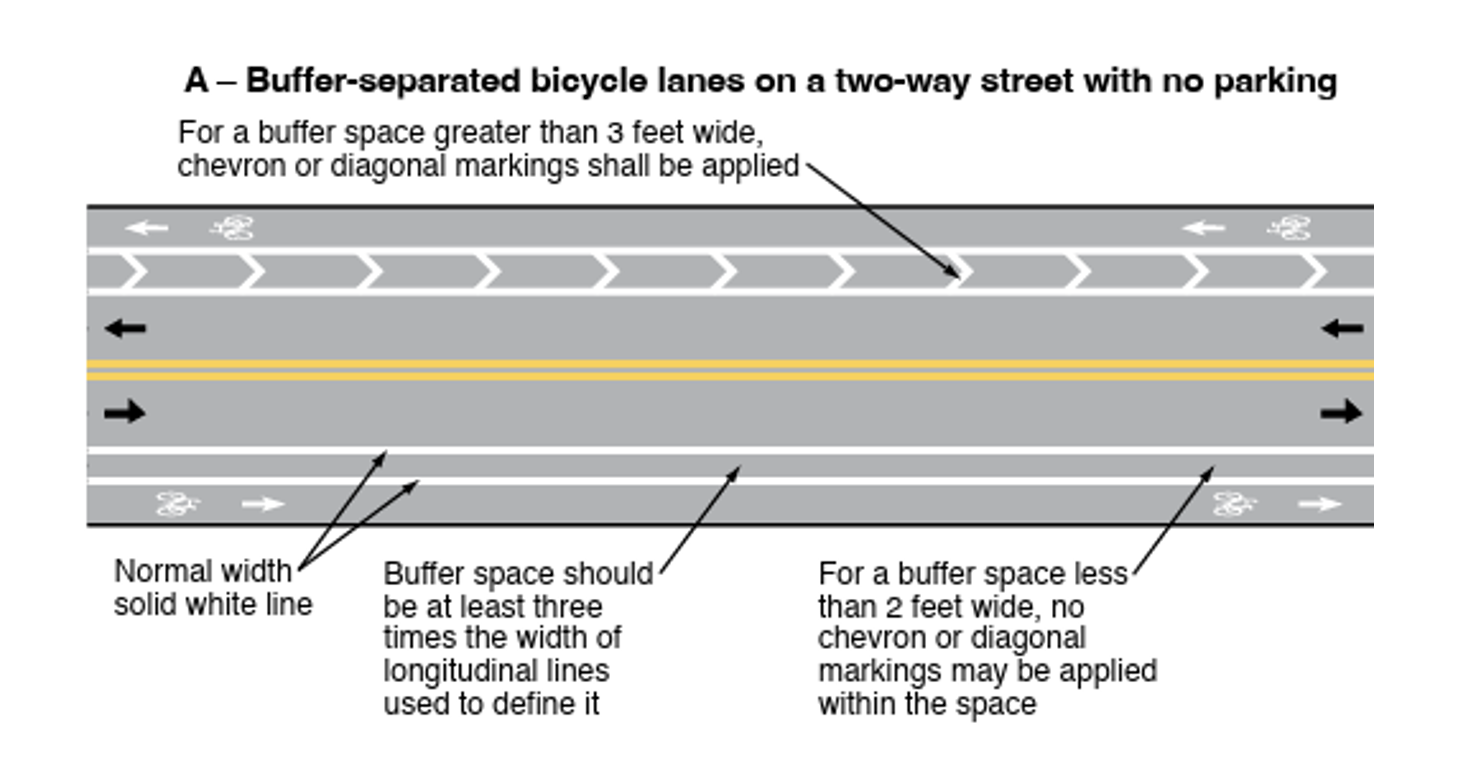
Image Source: MUTCD, 11th Edition, Figure 9E-6
Complimentary Countermeasures
- Evaluate and Implement Roadway Reconfiguration
- Colored Pavement
- Protected Intersections
REFERENCES AND RESOURCES
FHWA. Proven Safety Countermeasures. https://highways.dot.gov/safety/proven-safety-countermeasures/bicycle-lanes
FHWA. (CMF ID: 11296) Developing CMFs for Separated Bicycle Lanes. FHWA-HRT-23-025, (2023).
KYTC Complete Streets, Roads and Highways Manual (2022). https://transportation.ky.gov/BikeWalk/Documents/Complete%20Streets,%20Roads,%20and%20Highways%20Manual.pdf
CONTACT:
Chris VanDyke
Research Scientist | Program Manager
chrisvandyke@uky.edu


