Curb Extensions
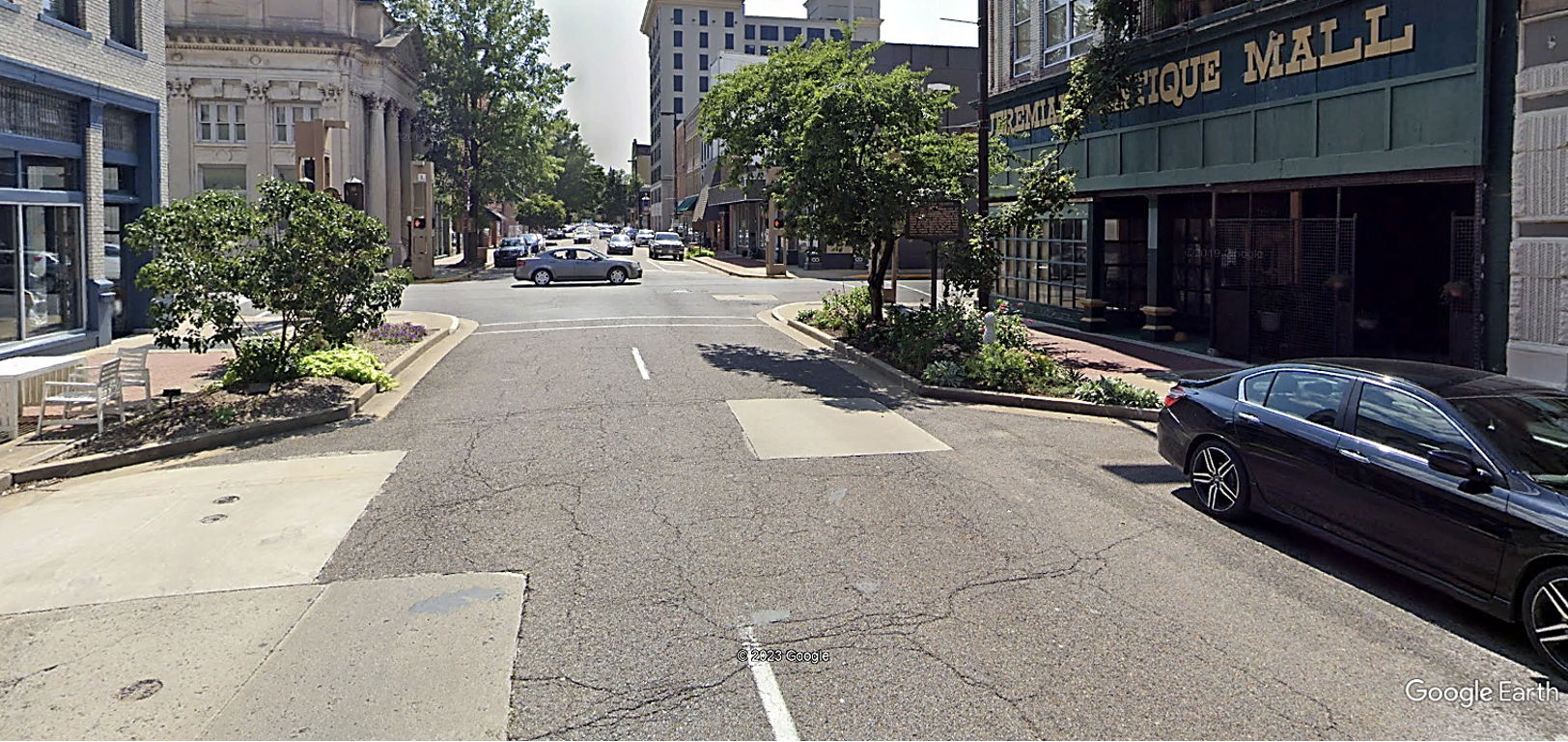
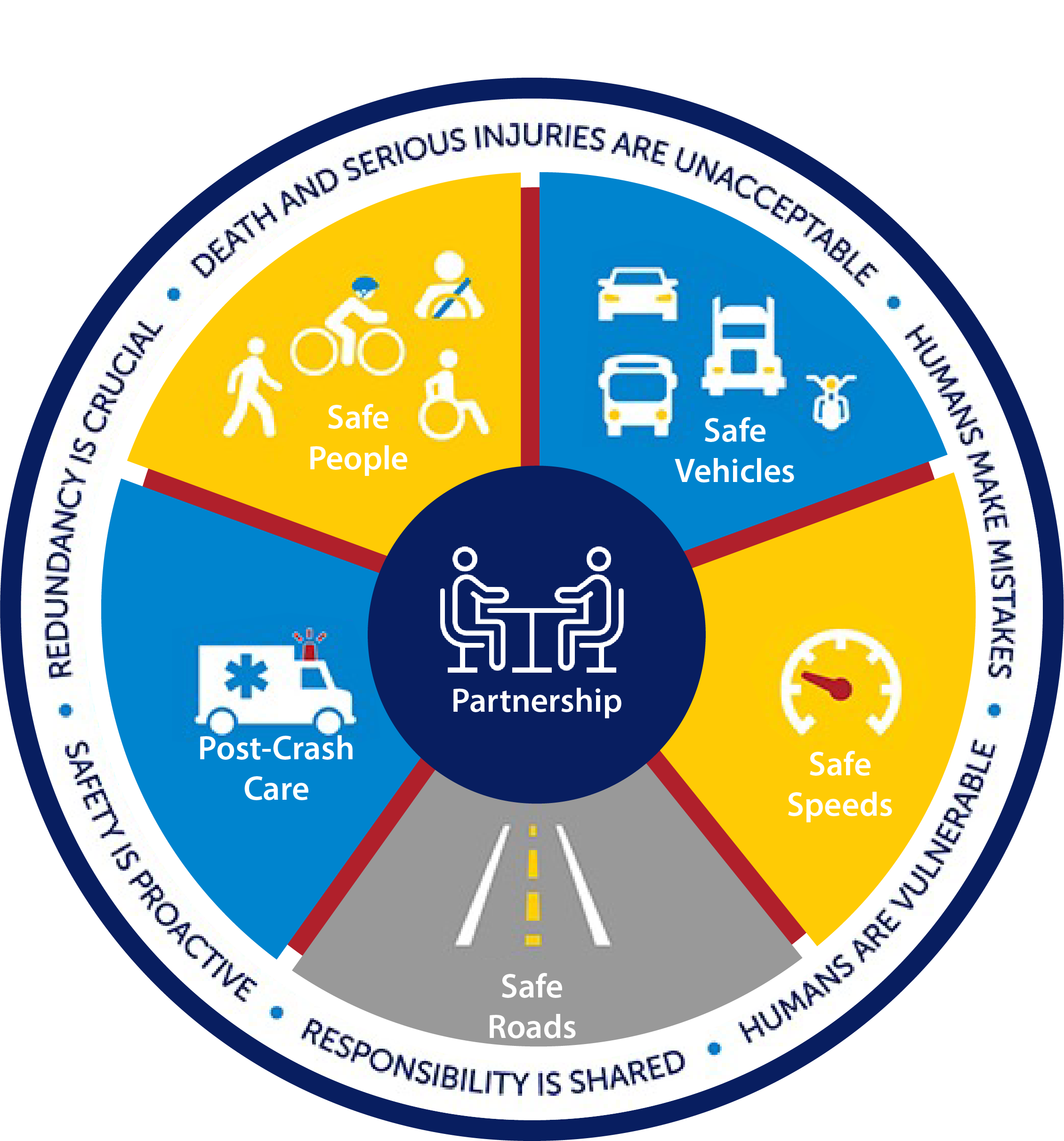

Image Source: Google Earth, Paducah
DEFINITION AND DESCRIPTION
A curb extension is a horizontal extension of the sidewalk into the street that results in a narrower roadway section. It may be used at intersection corners or mid-block. A curb extension at an intersection is called a corner extension or bulbout. A curb extension located mid-block is called a choker.
Curb extensions increase pedestrian visibility, reduce the distance pedestrians need to travel across a roadway, and encourage pedestrians to cross at designated locations. They also tighten intersection curb radii, encourage slower turning speeds, and prevent vehicles from parking at corners.
Implementation Categories
| Area(s) | Design and Geometrics, HSIP |
| Safety Category | 1, 2 |

CONSIDERATIONS
- Applied on curbed roadways.
- Consider drainage and utility impacts in design.
- May not be appropriate on intersection corners with significant turning volumes of large vehicles. If used, the stop bar on the opposite travel lane on the receiving leg of the intersection may need to be recessed to accommodate large vehicles making a turn.
- Generally, not appropriate along primary access routes to commercial or industrial sites or on high-speed rural intersections.
- Tactical curb extensions can be fabricated using low-cost, quick-build materials such as pavement markings and vertical delineators. The gutter can be spanned.
- KYTC Maintenance Agreements with cities often delegate KYTC’s maintenance responsibility to the roadway features between the curbs. Local governments usually maintain the features within right-of-way that are outside of the curbs (e.g. sidewalks).
APPLICATION
- May be used:
- In urban and rural town contexts at pedestrian crossings of curbed roadways
- For local, collector, and arterial streets
- At intersections and midblock crossings
- Recommended at locations with permanent on-street parking.
- In general, extensions should span the width of the shoulder or parking lane. Do not extend curb extensions into bicycle lanes.
- Provide an adequate shy distance between the curb and the travel lane.
example
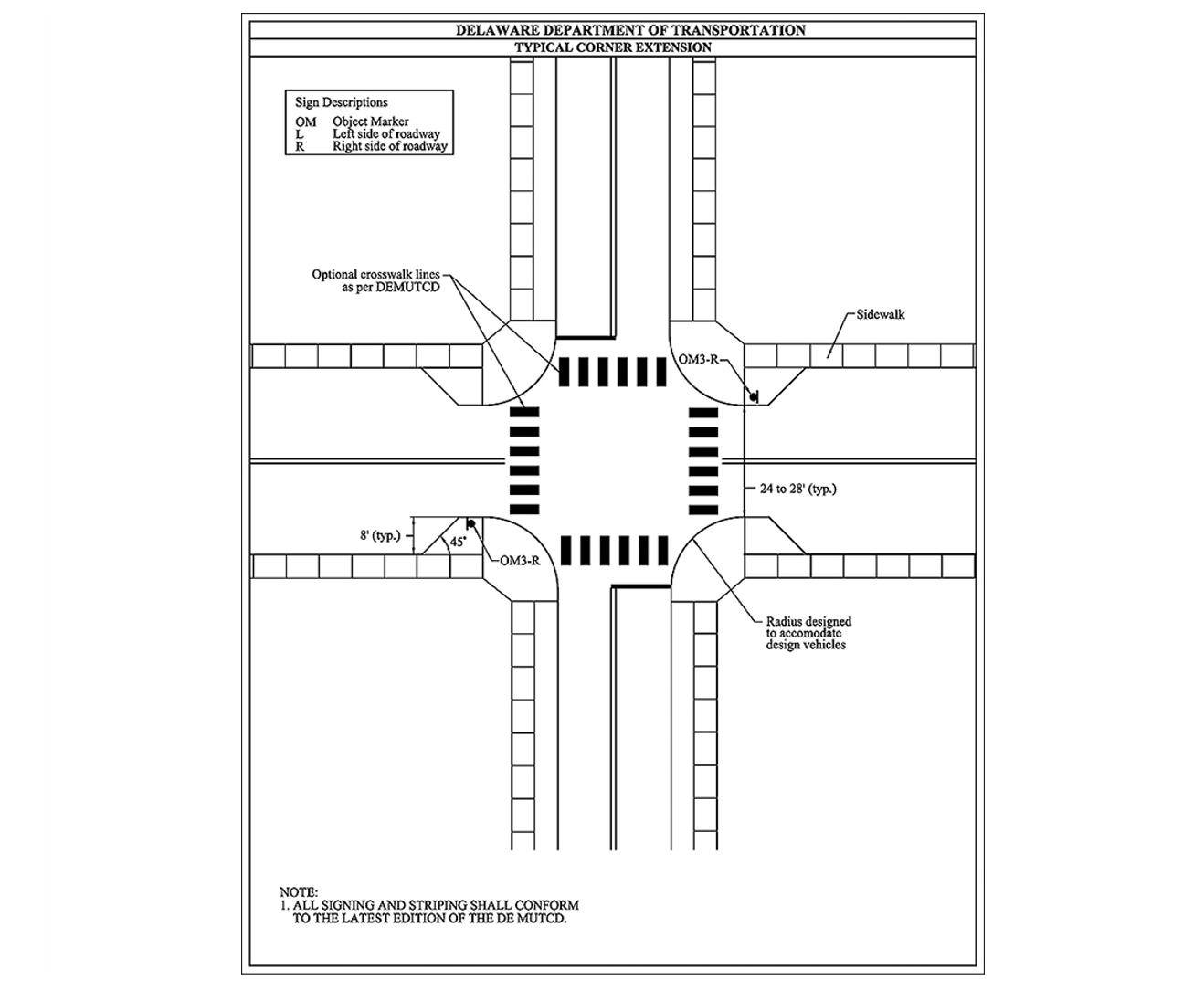
Image Source: Delaware DOT
Complimentary SSA Strategies
- Speed Tables and Raised Crosswalks
- Leading Pedestrian Interval
- Centerline Turn Hardening
- Lighting
- Evaluate and Implement Road Reconfigurations
- RRFB
REFERENCES AND RESOURCES
FHWA. Safe System Roadway Design Hierarchy. January 2024. FHWA-SA-22-069. https://highways.dot.gov/sites/fhwa.dot.gov/files/2024-01/Safe_System_Roadway_Design_Hierarchy.pdf
NACTO. Don’t Give Up at the Intersection – Protected Intersections. May 2019. https://nacto.org/publication/dont-give-up-at-the-intersection/protected-intersections/
CONTACT:
Chris VanDyke
Research Scientist | Program Manager
chrisvandyke@uky.edu


