Curve Widening
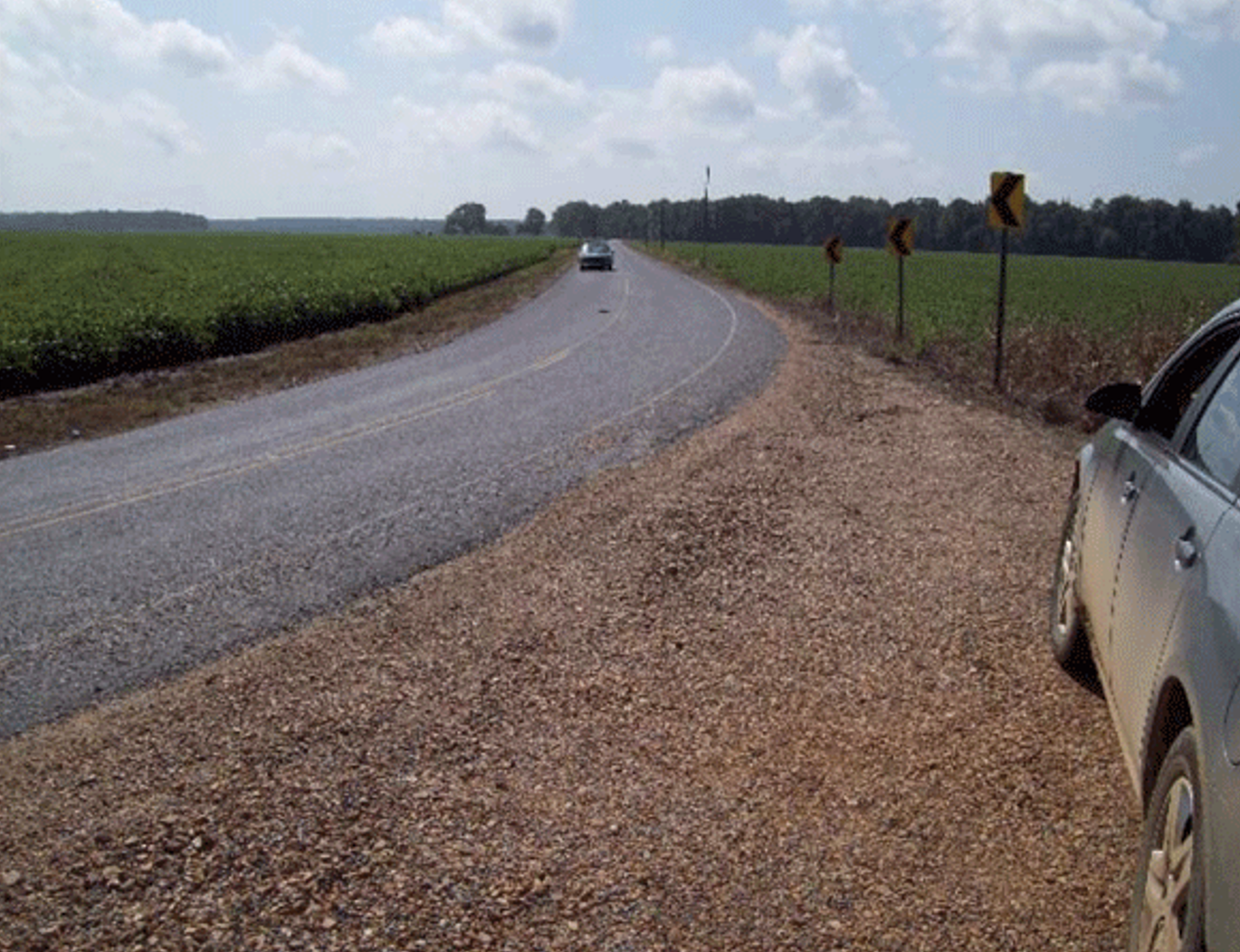

Image Source: FHWA
DEFINITION AND DESCRIPTION
When traversing a horizontal curve, the rear wheels of a motor vehicle track inside the front wheels, thereby making it difficult for a driver to hold the vehicle in the center of the lane. These problems become more pronounced on roads with narrow lanes and sharp curves. Adding or widening shoulders gives motorists a larger area in which to recover and regain control of their vehicles in the event of a roadway departure.
Implementation Categories
| Area(s) | Design & Geometrics |
| Safety Category | 1 |
CONSIDERATIONS
- Refer to Standard Drawing RGS-001, HDM 702.6, and Chapter 3 of the AASTHO Greenbook.
- Widen pavement by at least 2 feet as per RGS-100.
- Shoulder widening can occur on inside and outside shoulders.
- Maintain the striped width of the traveled lane.
APPLICATION
- Use on high-speed roadway curves with narrow shoulders.
- Stabilize widened shoulders and minimize steepening of roadside slopes.
example
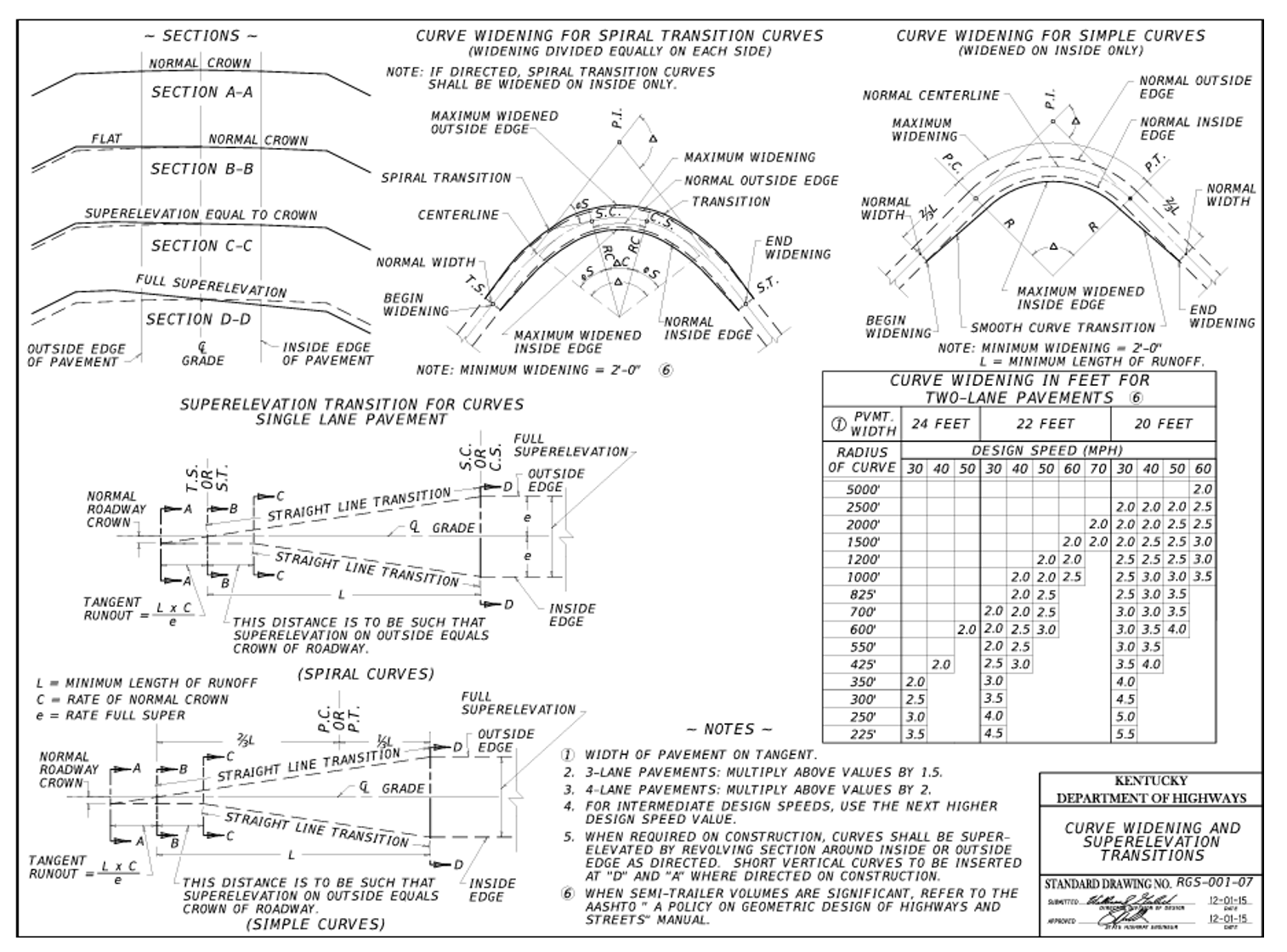
Image Source: KYTC Standard Drawings
Complimentary Countermeasures
- Slope Flattening
- Superelevation Correction
REFERENCES AND RESOURCES
AASHTO. A Policy on Geometric Design o Highways and Streets, 7th Edition. Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials, Washington DC, 2018.
FHWA. Proven Safety Countermeasure. https://safety.fhwa.dot.gov/provencountermeasures/roadside_design.cfm
FHWA. Low-Cost Treatments for Horizontal Curve Safety 2016. https://safety.fhwa.dot.gov/roadway_dept/countermeasures/horicurves/fhwasa15084/index.cfm#toc
KYTC Highway Design Manual, HD-702.6. https://transportation.ky.gov/Organizational-Resources/Policy%20Manuals%20Library/Highway%20Design.pdf
KYTC Standard Drawings (2020). https://transportation.ky.gov/Highway-Design/Standard%20Drawings%20DGNS%202020/00_Roadway_General.pdf
CONTACT:
Chris VanDyke
Research Scientist | Program Manager
chrisvandyke@uky.edu


